

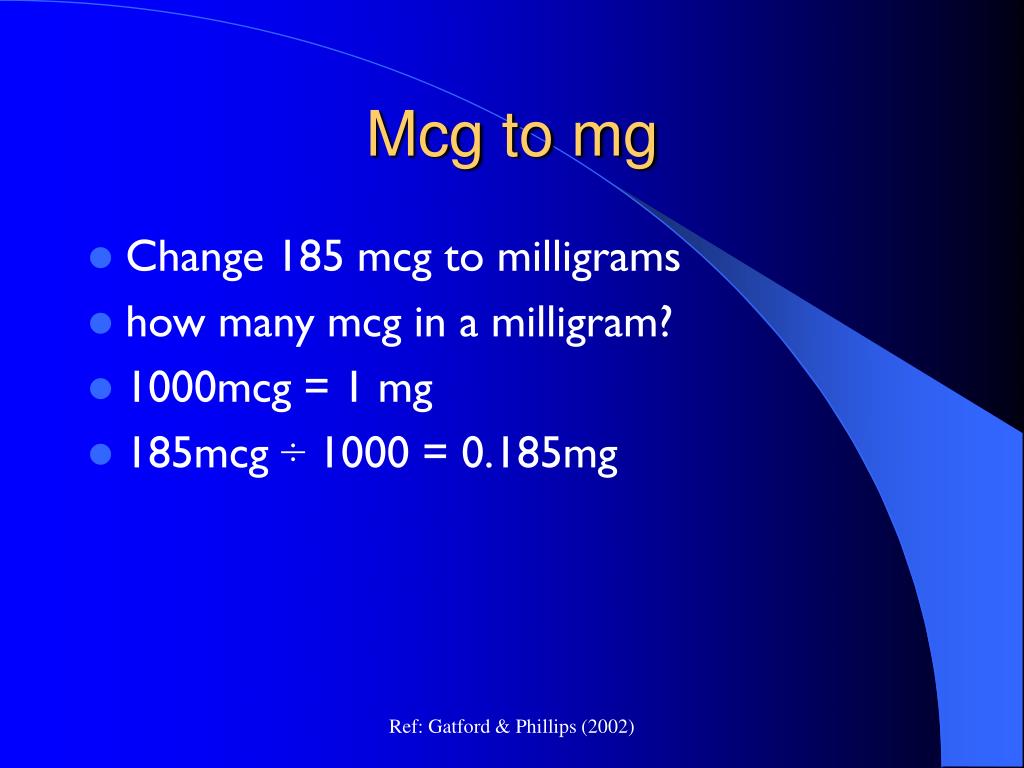
The milligram is the more frequently used unit of measurement due to its bigger size. Moreover, a milligram is a thousandth of a gram. This means that a milligram is 1000 times bigger than a microgram. On the other hand, the milligram is the long form of the abbreviation “mg.” One mg is equal to 1000 micrograms. A microgram is expressed as (μg) in usage. A microgram is a millionth of a gram, and it is the one of the smallest units of measurement, frequently used in microbiology tests, specifically in measurements for antibiotics like penicillin, oxacillin, and others. This implies that the microgram is smaller compared to a milligram. With reference to other units of measurement, a mcg is equal to. The term “mg” stands for the measurement of “milligrams,” while “mcg” stands for “micrograms.” Both units are used to measure an object’s mass and to indicate an object’s weight. Dietary niacin can come in several forms, and the new unit accounts for tryptophan as a source of niacin.The terms “mg” and “mcg” are both abbreviations for small units of measurement in the metric system. New guidelines require that niacin be reported as Niacin Equivalents (NE). Folic acid has greater bioavailability than naturally occurring folates. New guidelines require that folates/folic acid be reported in Dietary Folate Equivalents (DFE) with mcg of folic acid in parentheses. Previously all folates and folic acid were reported as mcg folic acid. Folateĭietary folate can come in different forms naturally occurring folates and synthetic folic acid.
New guidelines require that vitamin D be reported in mcg rather than IU. To convert from IU to mg alpha-tocopherol, use the 2 steps listed in the table, above. Vitamin E in food and dietary supplements can come from natural or synthetic forms. New guidelines require that Vitamin E content be determined based on the source of vitamin E and that it be reported as mg alpha-tocopherol rather than in IU. To convert from IU to RAE, use the 2 steps listed in the table, above. New labeling guidelines require reporting of vitamin A in the unit of mcg RAE, (retinol activity equivalent) in order to account for the differing bioavailability of the forms. Vitamin A has previously been reported in international units (IU). Some of these forms have greater bioavailability than others. Vitamin A in the diet can come in different forms: retinol, beta-carotene, alpha-carotene, and beta-cryptoxanthin. IU: International Unit is a measure of biological activity and is different for each substance. Labeling Units of Measure mcg: microgram. *The data in the DSID-4 are reported using the current FDA ingredient unit labeling.
For more information from the FDA, click here.ġ mcg RAE = 2 mcg supplemental beta-caroteneġ IU = 0.67 mg for d-alpha-tocopherol (natural)ġ IU = 0.9 mg for dl-alpha-tocopherol (synthetic)ġ mg vitamin E (as alpha-tocopherol) label claim = 1 mg of natural α-tocopherolġ mg vitamin E (as alpha-tocopherol) label claim = 2 mg of synthetic α-tocopherol The FDA will permit manufacturers to include the amounts of nutrients in the old units in parentheses adjacent to the amounts in the new units. The changes that will affect the application of DSID results are the changes in the units used to declare vitamins and minerals on supplement labels. Voluntary compliance prior to that date is permitted, and it is expected that there will be a period of time when both types of labels will be on the market. The new regulations will be mandatory in 2019-2020. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced regulations that require amendments to the existing supplement facts label, which uses units and conversions based on the 1968 Recommended Daily Allowances (RDA).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
